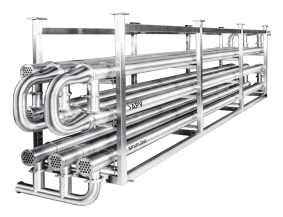
How do tube heat exchangers work?
Tube heat exchangers operate on the principle of conduction, which involves the transfer of heat from a hot fluid to a cooler fluid through the walls of a series of tubes or pipes. These heat exchangers are commonly used in industries such as chemical, petrochemical, food processing, and power generation due to their high efficiency, and ease of maintenance. The efficiency of tube heat exchangers depends on factors such as flow rate, temperature, viscosity, and thermal conductivity of the fluids, as well as the design of the heat exchanger itself. Tube heat exchangers can be configured in different ways, including single-pass, multi-pass, shell and tube, and plate and frame.
Advantage of tube heat exchangers
Tube heat exchangers offer important advantages over other types of heat exchangers. Some of the key benefits of tube heat exchangers include high efficiency and versatility
Tube heat exchangers are highly efficient in transferring heat between two fluids. The use of tubes creates a large surface area for heat transfer, which enhances the heat transfer rate and results in higher efficiency.
Tube heat exchangers can also be used in a variety of applications, including HVAC systems, chemical processing, refrigeration, and power generation. They can handle a wide range of temperatures and pressures, making them versatile and adaptable to different applications.
Industries and applications that uses tube heat exchangers
Tube heat exchangers are widely used in various industries and applications that require efficient heat transfer. Some of the common industries and applications that use tube heat exchangers include:
- Chemical Processing: Tube heat exchangers are used in the chemical processing industry for heating and cooling of process fluids. They are often used for applications such as condensing, reboiling, and vaporizing of various chemicals.
- Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems: Tube heat exchangers are used in HVAC systems for heating and cooling of air and water. They are commonly used in air handling units, chiller systems, and heat pumps.
- Power Generation: Tube heat exchangers are used in power plants for cooling of steam, gas, and other fluids in the power generation process. They are also used in heat recovery systems to extract heat from exhaust gases and convert it into useful energy.
- Food and Beverage Processing: Tube heat exchangers are used in the food and beverage industry for heating and cooling of food products and processing fluids. They are commonly used in pasteurization, sterilization, and cooling of various food products.
- Oil and Gas: Tube heat exchangers are used in the oil and gas industry for heating and cooling of crude oil, natural gas, and other fluids. They are commonly used in refineries, petrochemical plants, and offshore platforms.
Important considerations when selecting tube heat exchangers
When selecting a tube heat exchanger, there are several important considerations to keep in mind to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Some of the key factors to consider include:
- Operating Conditions: It is important to consider the operating conditions of the heat exchanger, including temperature, pressure, and flow rate. The heat exchanger must be designed to withstand specific operating conditions to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance.
- Fluid Properties: The properties of the fluids being transferred, including viscosity, density, and corrosiveness, must be considered when selecting a tube heat exchanger. The heat exchanger must be designed to handle the specific properties of the fluids to prevent damage and ensure efficient heat transfer.
- Tube Material: The material of the tubes is an important consideration as it can affect the performance and lifespan of the heat exchanger. Common materials include copper, stainless steel, and titanium, each with their own advantages and disadvantages.
- Design and Size: The design and size of the heat exchanger must be carefully considered to ensure it meets the specific requirements of the application. The heat exchanger should be designed to minimize pressure drop and optimize heat transfer efficiency.
- Maintenance and Cleaning: The ease of maintenance and cleaning is an important consideration, as it can affect the lifespan and performance of the heat exchanger. The heat exchanger should be designed for easy access and cleaning to prevent the buildup of contaminants and ensure optimal performance.
Why buy tube heat exchangers from AxFlow
AxFlow offers tube heat exchangers for the widest range of industries and applications. Only at AxFlow do you receive individual advice from industry-experienced process engineers and the manufacturer-independent selection of the world's leading process technology. Do you need support in selecting the right pump for your needs? Do not hesitate to get in touch. AxFlows experts and engineers can provide guidance for selecting, specifying, installing, and maintaining your fluid handling equipment.